Butterfly hug therapy on reducing anxiety levels and stabilization hemodynamics in patient digital subtraction angiography
Downloads
Background: Digital subtraction angiography can affect anxiety in patients so that it can worsen the patient's condition during catheterization, such as increased heart rate and breathing. One of the efforts to reduce anxiety that can improve hemodynamics is butterfly hug therapy. However, its effectiveness in reducing hemodynamic anxiety needs to be further investigated.
Purpose: To evaluate butterfly hug therapy's effectiveness on anxiety and hemodynamics before digital subtraction angiography.
Methods: This is a quasi-experiment study with a pretest-posttest control group design. Fifty-two respondents were selected using purposive sampling. A total of 26 respondents were given butterfly hug therapy, and 26 others were given standard therapy. The study implemented the Zung Self Rating Anxiety Scale Questionnaire and observation sheet. This research analysis uses the Independent T-test and Wilcoxon Test.
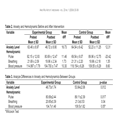
Results: The anxiety level of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group (46.73 ± 2.08 vs. 53.84 ± 1.74; p<0.05). In hemodynamic stability (pulse, respiratory, and blood pressure) was stability than the control group (80.69 ± 2.44 vs. 89.11 ± 2.39; 20.65 ± 0.39 vs. 21.0 ± 0.53; 104.7 ± 1.46 vs. 109.5 ± 1.82; p <0.05).
Conclusion: Butterfly hug therapy is effective in reducing anxiety and stabilizing hemodynamics among patients undergoing digital subtraction angiography.Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.