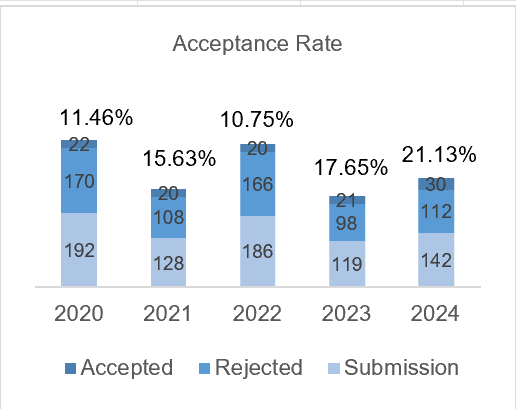
In vivo study on the effect of astaxanthin cream on preventing inflammation in skin tissue exposed to acute UVB by reducing MDA and IL-6 levels
Downloads
Background: Continuous UVB exposure induces lipid peroxidation and inflammation, with Malondialdehyde (MDA) as an indicator, leading to interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion. Astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant, is 50-100 times stronger than vitamin C, but its effects on MDA and IL-6 in UVB exposed skin have not been studied.
Objective: This study aims To determine the effect of astaxanthin cream on MDA and IL-6 levels in individuals exposed to acute UVBrays.
Methods: An experimental post-test-only control group design with four groups: healthy (K1), negative control (K2), and two treatment groups (K3, K4) exposed to UVBand given 0.05% and 0.1% astaxanthin cream, respectively. UVBirradiation was at 302 nm for 15 minutes, 5 days. MDA levels were measured using the TBARS method, and IL-6 levels were measured using ELISA. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and ANOVA tests.
Results: Average MDA levels were K1 (0.688 nmol/mL), K2 (0.766 nmol/mL), K3 (0.486 nmol/mL), and K4 (0.731 nmol/mL), with significant differences found (p=0.001). Average IL-6 levels were K1 (8.78 ng/L), K2 (6.23 ng/L), K3 (6.49 ng/L), and K4 (7.59 ng/L), with significant differences (p=0.003).
Conclusion: Astaxanthin cream reduces MDA and IL-6 levels following acute UVB exposure.
Copyright (c) 2025 MEDISAINS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.