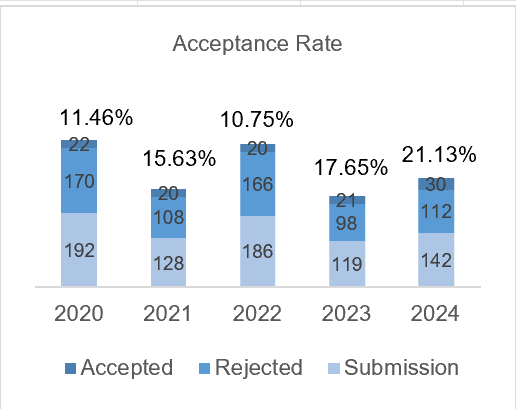
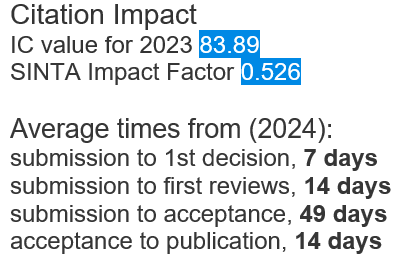
Antifertility effect of betel nut (Areca catechu L) in male rat

Downloads
Additional Files
Background: Betel nut (Areca catechu L) are traditional beverages in Jambi. Betel nut high dose has a cytotoxic effect on testis and other organs—limited data about the effect of betel nut as male antifertility.
Purposes: This study aimed to determine the effect of infertility on betel nut use at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight (BW) in male rats.  Â
Methods: Ten male Sprague Dawney rats that had passed the fertility test, aged 2-3 months and weighing 150-200 grams ware used in this study. The rat was grouped into two groups randomly. Group 1, as the negative control, were received aqua dest, and group 2 was treated by betel nut with dose 50 mg/kg BW for 35 days. When terminated, testis weight weighed using micro scales. Blood collected for measuring testosterone levels. Histopathology assessment of testis used Hematoxylin Eosin Staining and sperm counting from cauda epididymis.
Results: The weight of testis in the group received betel nut was lower than the control group. The histopathology of testis showed shrunk, reduced the diameter of seminiferous tubules, and like cytolytic lesions in the germinal layer—the total sperm number and progressive sperms also lower than the control group (p<0.05). There was no abnormality in Leydig cell and interstitium tissue. Male rats after treatment could not impregnate the female rats.
Conclusion: Betel nut at dose 50 mg/kg BW have antifertility activity in male rats.Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.