Analysis of procalcitonin and urine nitrite to predictor sepsis patients
Downloads
Background: Sepsis is a significant health problem worldwide. Various sepsis biomarkers have been studied before, but few data link PCT and urinary nitrite levels to culture result in septic patients.
Purposes: This study compares PCT, Urine Nitrite on culture results against their sensitivity to determine variables that can be used to predict sepsis patients.
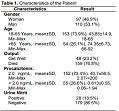
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study by taking data on patients with sepsis aged ≥18 years in 207. Diagnostic tests were performed to determine sensitivity and specificity of PCT, Urine Nitrite, and Blood Culture of septic patients. A Chi-square test was carried out to see the relationship between two parameters and the outcome of sepsis.
Results: PCT sensitivity was higher than Urine Nitrite: 74.5%. Specificity of Urine Nitrite was higher than PCT: 88.2%. Procalcitonin has a significant relationship with sepsis patient outcomes (p<0.005).
Conclusion: PCT can predict septic patients because it has a higher sensitivity than urine nitriteAuthors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.