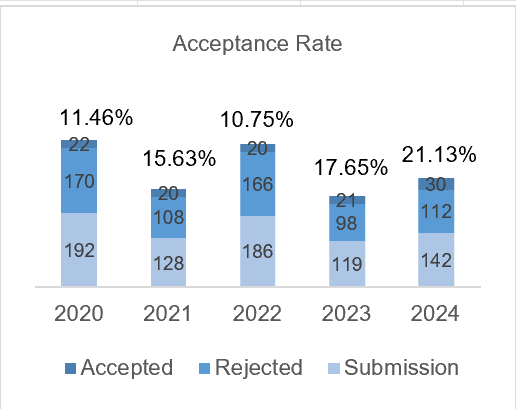
In vivo study: effect of black cumin seeds extract (Nigella sativa Linn.) on wound healing
Downloads
Background: Wound healing is a complex biological process involving inflammatory, proliferative, and remodelling phases. The increasing interest in natural therapies has led to the exploration of black cumin (Nigella sativa) for its immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. While previous studies have examined Nigella sativa effects on acute wounds, limited research has assessed its impact on leukocyte levels and its efficacy compared to conventional treatments.
Purpose: This study evaluates the effects of Nigella sativa seed extract on incisional wound healing and leukocyte levels in Rattus norvegicus, determining its potential role in accelerating tissue regeneration and modulating inflammation.
Methods: A true experimental study with a posttest-only control group design was conducted using 24 male Wistar rats, divided into four groups: negative control (distilled water), positive control (povidone-iodine), and two treatment groups receiving Nigella sativa extract once or twice daily. Wound area reduction was measured on days 7 and 14, and leukocyte levels on day 7. Statistical analysis included Kruskal-Wallis, One-way ANOVA, and post hoc tests (p < 0.05).
Results: Nigella sativa-treated groups exhibited significantly faster wound closure than controls. By day 14, complete closure was observed in both treatment groups, while residual wounds remained in controls. Leukocyte levels were significantly higher in the treatment groups than in the negative control (p = 0.001), indicating an enhanced immune response. No significant difference was found between once- and twice-daily treatments (p = 0.166 for wound area, p = 0.996 for leukocytes).
Conclusion: Nigella sativa extract accelerates wound healing by promoting wound contraction and modulating immune responses. The findings support its potential as a natural alternative for wound management, with effects comparable to povidone-iodine.
Purnama, H. & Ratnawulan, S. Review Sistemik: Proses Penyembuhan Dan PPerawatan Luka. (2017).
S. Anindyka Mentar. Gambaran Perubahan Patologi Anatomi Yang Diberi Gula Dan Madu Sebagai Alternatif Pengobatan Luka Sayat Pada Kucing Domestik (Felis Omestica).
Eufrasia, V., Umilia Pratiwi, N. & Susanti, R. Uji Efektivitas Penyembuhan Luka Sayat Ekstrak Rimpang Jeringau Merah (Acorus Sp.) Pada Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus) Galur Wistar. (2015).
Khasanah, M. N., Harjoko, A. & Candradewi, I. Klasifikasi Sel Darah Putih Berdasarkan Ciri Warna dan Bentuk dengan Metode K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN). IJEIS 6, 151–162 (2016).
Belgaumi, U. I., Patil, S., Gandhi, J. M. & Shete, A. S. The Many Therapeutic Applications of Nigella sativa - A Review of Literature. J Evol Med Dent Sci 9, 2151–2157 (2020).
Hannan, M. A. et al. Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety. Nutrients vol. 13 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061784 (2021)
Sallehuddin, N., Nordin, A., Idrus, R. B. H. & Fauzi, M. B. Nigella sativa and Its Active Compound, Thymoquinone, Accelerate Wound healing in an In Vivo Animal Model: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health vol. 17 1–17 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17114160 (2020).
Ikhsan, M. Habbatussauda Dalam Peningkatan Imun Di Masa Covid-19. Jurnal Riset Agama vol. 1 (2021).
Nurhayati. Pemberian Jintan Hitam (Nigella Sativa L) dan Madu (Apis Mellifera) Sebagai Suplemen Zat Besi dalam Meningkatkan Kadar Hemoglobin Ibu Hamil. SIMFISIS Jurnal Kebidanan Indonesia 2, 327–335 (2022).
Kmail, A., Said, O. & Saad, B. How Thymoquinone from Nigella sativa Accelerates Wound Healing through Multiple Mechanisms and Targets. Curr Issues Mol Biol 45, 9039–9059 (2023).
Thakur, S., Kaurav, H. & Chaudhary, G. Nigella sativa (Kalonji): A Black Seed of Miracle. International Journal of Research and Review 8, (2021).
Baqi, M. F. A. Al-Lu’lu Wal Marjan. Shahih Bukhari Muslim (Usman, Muhammad Ahsan Bin. Penerjemah). http://pustaka-indo.blogspot.com (2017).
Inayah, N., Program Studi Keperawatan, M. & Pengajar Keperawatan UNTAN, S. Efektifitas Madu Dan Jintan Hitam Terhadap Penyembuhan Luka Akut Pada Tikus Wistar Di Laboratorium Hewan Uji Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Tanjungpura Oleh. (2015).
Febrianto, V., Bulan, S. & Lesmana, D. Effect of Black Cumin Extract (Nigella sativa Linn.) on Closure Time of Incision Wound in Swiss Webster Mice. e-GiGi 10, 109 (2022).
Sari, W., Chiuman, L., Ginting, S. F. & Ginting, C. N. Pengaruh Krim Ekstrak Jintan Hitam (Nigella Sativa) Terhadap Kadar Kolagen Dan Hidrasi Kulit Tikus (Rattus Norvegicus) Galur Wistar Jantan Yang Dipapar Sinar Ultraviolet-B. vol. 19 (2020).
Karini, N. D., Amalina, R. & Styaningrum, Y. Effect Of Black Nanoemulgel (Nigella Sativa) On The Number Of Fibroblas In Healing The Wound After Dental Cutting In Rats. 6, (2024).
Saputra, A. Efektivitas Ekstrak Nigella Sativa Dan Bubuk Kopi Untuk Penyembuhan Luka Sayat Pada Tikus Putih. (2021).
Zikriah. Uji Imunomodulator Ekstrak Etanol Jinten Hitam (Nigella Sativa L.) Terhadap Jumlah Total Leukosit, Persentase Limfosit, Persentase Monosit Dan Kadar Interleukin-β Pada Mencit BALB/c. (2014).
Suhatri & Aldi, Y. Aktivitas Ekstrak Etanol Biji Jintan Hitam (Nigella sativa Linn.) Terhadap Titer Antibodi Dan Jumlah Sel Leukosit Pada Mencit Putih Jantan. SCIENTIA 1, (2011).
Suriadi, Hastuti, L. & Handayani, L. W. Efektifitas Pemberian Madu Pinang Muda, Dan Jintan Hitam Dalam Proses Penyembuhan Luka Kronik Dengan Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pada Tikus Putih. Jurnal Keperawatan dan Kesehatan 6, (2015).
Copyright (c) 2025 MEDISAINS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.